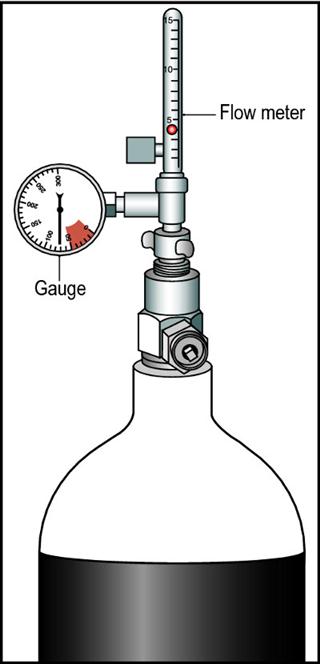
oxygen delivery devices and flow rates uk
Delivery to the paent. Low flow O2 delivery device 05-6 Lmin.
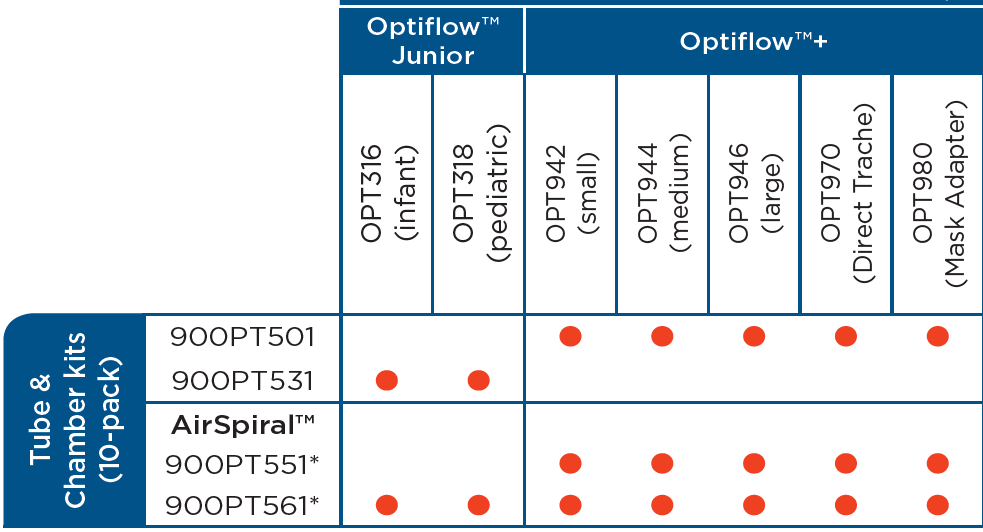
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery
Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates should be adjusted to keep the oxygen saturation in the target range.
. Lmin 1 Resultant oxygen concentration. Give oxygen therapy in a way which prevents excessive CO 2 accumulation - ie. Diving and Hyperbaric Medicine.
Nasal Cannula 1-6 litersminute 25-50 Humidifier recommended for all flow rates 4 litersminute High Flow Nasal Cannula 1-15 litersminute 25-50 High. Per minute will deliver approximately 24. In these situations supplemental oxygen can be administered via various oxygen delivery devices ranging from nasal prongs to invasive ventilation.
Can delivery precise and dependable FiO2. 26Lmin gives approx 2450 FIO2. 1 to 6 liters.
A minimum of 6 Lminute of oxygen flow is needed 2to prevent rebreathing of exhaled carbon dioxide. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates should be adjusted to keep the oxygen saturation in the target range. Low flow device Most common device used for mild hypoxia Can be set between 1 and 6 LPM 24 to 40 FiO2 FiO2 increases approximately 4 with each liter of O2 KorupoluR GJ Needham DMContemporary CriticalCare.
The oxygen flow rate and the FiO2. The flow rate is how many liters of oxygen per minute your device delivers. Monitoring and maintenance of target saturation Oxygen saturation and delivery system including flow rate should be recorded on the patients monitoring chart.
What is a nasal cannula. If you need a higher flow rate of oxygen its likely you will need a face mask. Oxygen saturation and delivery system including flow rate should be recorded on the patients monitoring chart.
For example patients commonly use a flow rate of 2 liters per minute but the flow rate varies by each patients needs. High-concentration normobaric oxygen O 2 administration is the first-aid priority in treating divers with suspected decompression illness. Only goes up to 60 FIo2 so not for patients who have significantly high oxygen demands bulky.
A simple face mask can deliver 35 to 60 oxygen with an appropriate flow rate of 6 to 10 Lminute. Reduce the work of breathing. 2 to 15 Lmin.
It is NOT the Lmin stated on the venturi that is delivered to the patient. Designed to entrain a set amount of O2 and air which combine to produce a set flow of O2 the stated on the venturi. Discuss the different options with your respiratory specialist.
Selection of the appropriate flow rate and delivery device. A nasal cannula can be used to deliver up to six litres of oxygen a minute comfortably. 22 to 60 oxygen with appropriate oxygen flow rates of 05 to 2 Lminute.
Oxygen flow through a TTOC ranges between 05 and 4 Lmin 1. This article presents an overview of oxygen devices oxygen concentrators compressed gas cylinders and liquid oxygen and delivery systems high- and low-flow. The nasal cannula is a device that has two prongs that are placed in the patients nostrils and deliver oxygen at flow rates of 1 to 6 liters per minute.
There are two important things to consider when delivering supplemental oxygen to your patient. 1L 24 2L 28 3L 32 4L 36 5L 40 6L 44. Recommended in the Guideline as suitable for most paBents with both type I and II respiratory failure.
Deliver oxygen to paents. Prompt clinical assessment is required if oxygen therapy needs to be initiated or increased due to a falling saturation level. Ensure adequate clearance of secretions and limit the adverse events of hypothermia and insensible water loss by use of optimal humidification dependent on mode of oxygen.
2 A simple face mask is a low-flow oxygen device. Oxygen delivery by TTOC bypasses the anatomical dead space in the upper airways and mouth allowing oxygen to pass directly into the trachea. Adapters deliver set amounts of FiO2 at 24 to 60.
Oxygen use has extended from inpatient to outpatient settings for patients with chronic pulmonary diseases and complications of hypoxaemia. Oxygen Delivery Devices Delivery Device Minimum to Maximum Liter Flow Range Adults Approximate O2 Delivered Notes RT assistance recommended for liter flows of 6 litersminute or more. A flow rate of 2 liters per minute increases the FiO2 from 21 percent room air to 28.
Nasal cannula Simple plastic tubing prongs with an over the ear adjustments. Nasal cannulae Teleflex Medica 1. Sizing available for adults children and infants.
The best O 2 delivery device and flow rate are yet to be determined. High capacity oxygen delivery device High capacity oxygen delivery devices capacity 250-1500 ml With these devices O 2 flows directly into the reservoir bag which fills whenever the patients inspiratory flow rate is lower than the flow rate of delivered O 2The patient thus inhales O 2 preferentially from the reservoir bag and ambient air is not entrained avoiding dilution of. Oxygen delivery devices and flow rates.
You can breathe in the oxygen from its container either through nasal cannula or a face mask. Oxygen delivery device Oxygen flow rate. Flow 5ltmin is less tolerated due to flow jet in nasal cavity 1 - 24 2 - 28 3 - 32 4 - 36 5 - 40 6 - 44.
Higher flows 4 Lmin make it uncomfortable for the patient. 1-2 with every increase in o2 flow per litre. Hudson Nonrebreather Teleflex Medical 1012 80100.
How much FiO2 you receive from your oxygen concentrator depends on your flow rate. FIO2 depends on oxygen flow and paents minute volume and inspiratory flow and paern of breathing. Different oxygen delivery devices to ensure oxygen is delivered safely.
Hudson mask Teleflex Medical 56. The type of delivery device you choose to use. 200969111 Bailey P Thomsen GE Spuhler VJ et alCrit Care MedJan2007351139145.
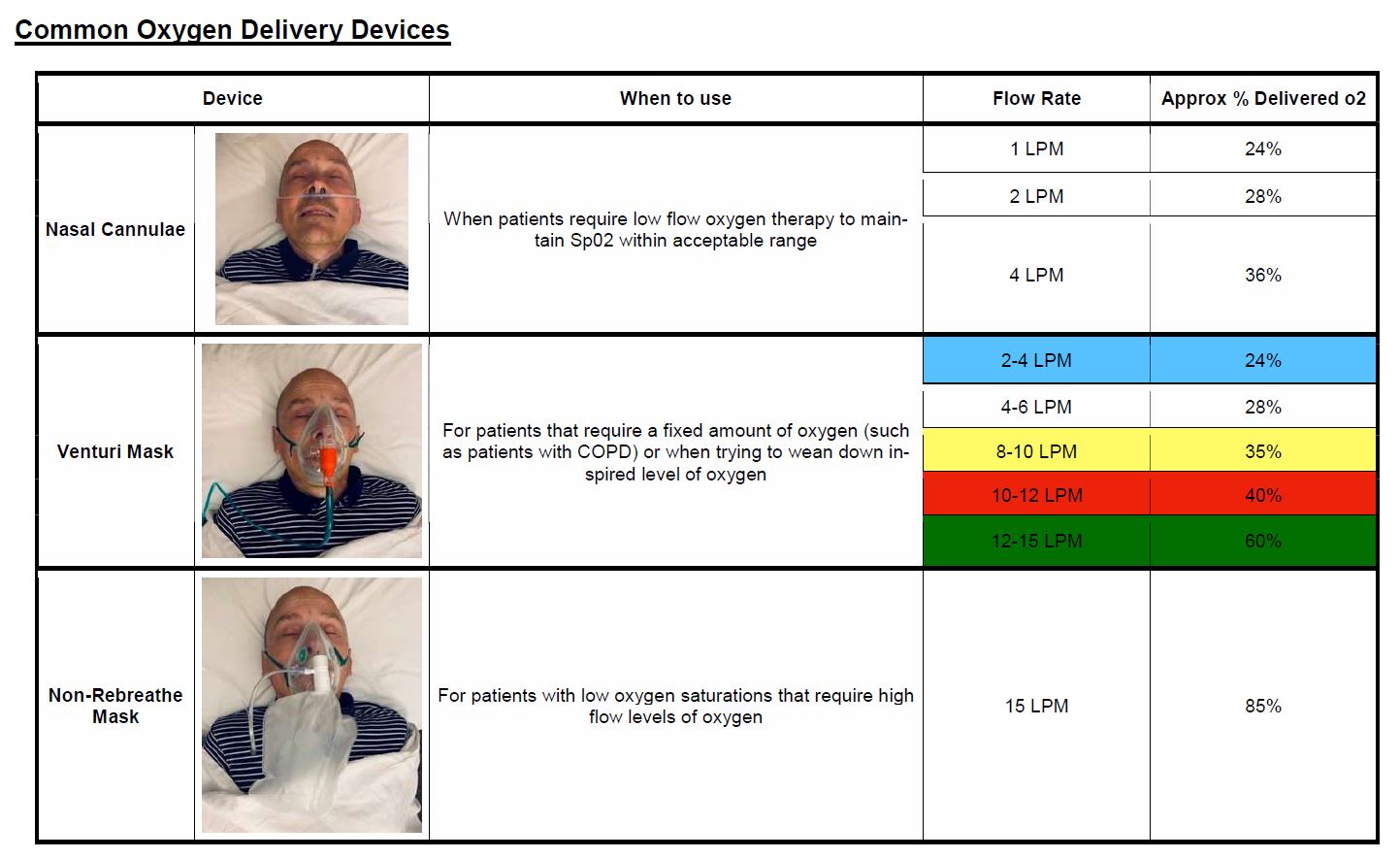
Medical Gases In Ed Rcemlearning
Mitchell Home Medical Referral Help
Oxygen Prescribing And Administration In Adults
Oxygen Prescribing And Administration In Adults
Clinical Guidelines Nursing Oxygen Delivery

Oxygen Delivery Devices And When To Use Them Emt Flashcards Quizlet

Oxygen Delivery Devices Ati Flashcards Quizlet

Pdf The Efficacy Of Oxygen Wafting Using Different Delivery Devices Flow Rates And Device Positioning

High Flow Noninvasive Ventilation And Awake Nonintubation Proning In Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 With Respiratory Failure Chest

Oxygen Delivery Devices Chapter 10 Diagram Quizlet
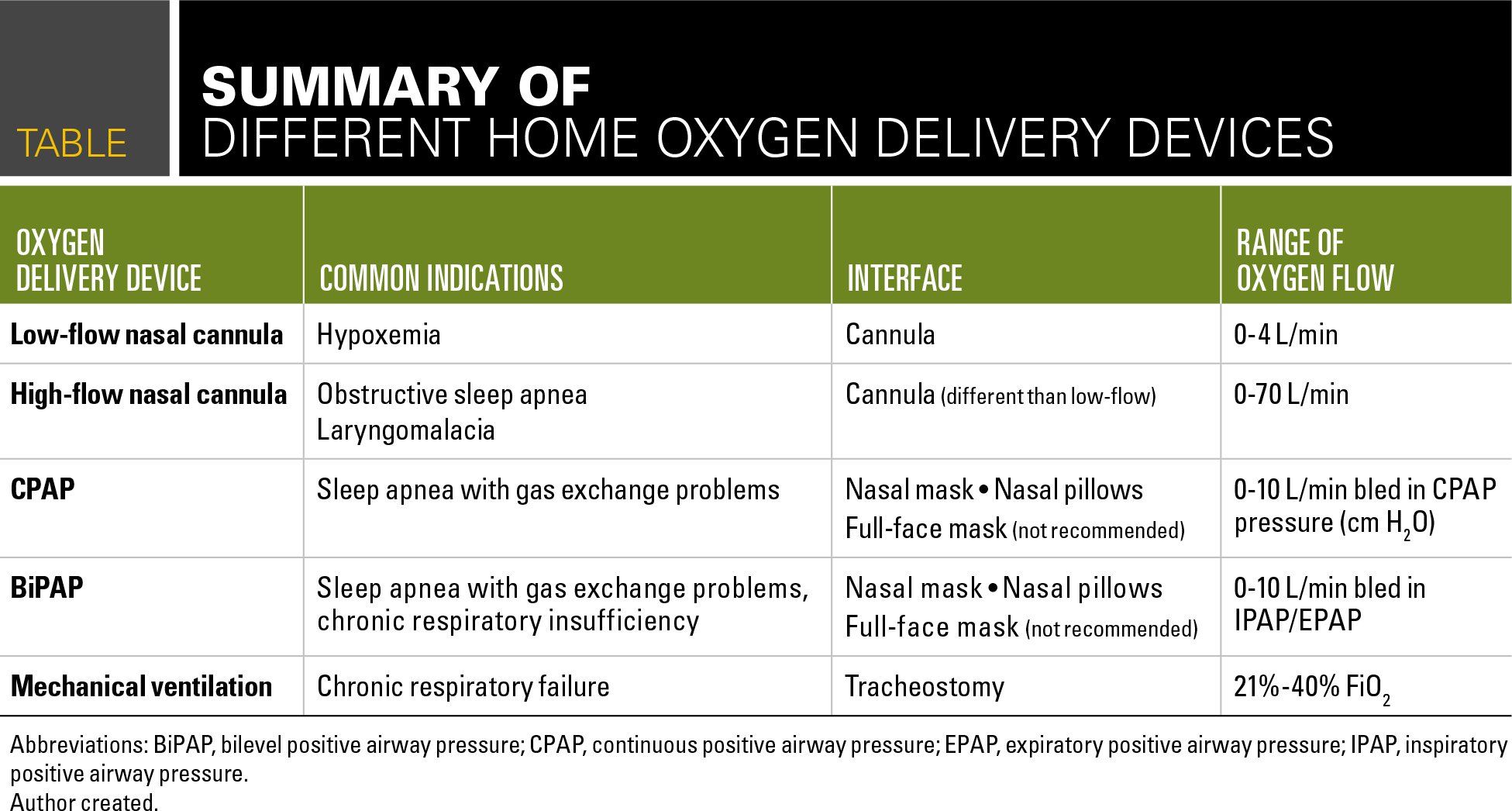
Oxygen Delivery In The Home Setting

Covid 19 And O2 Therapy Initial Prehospital Approach In Mild Symptomatic Patients Medest

Types And Characteristics Of Oxygen Delivery Devices Download Table